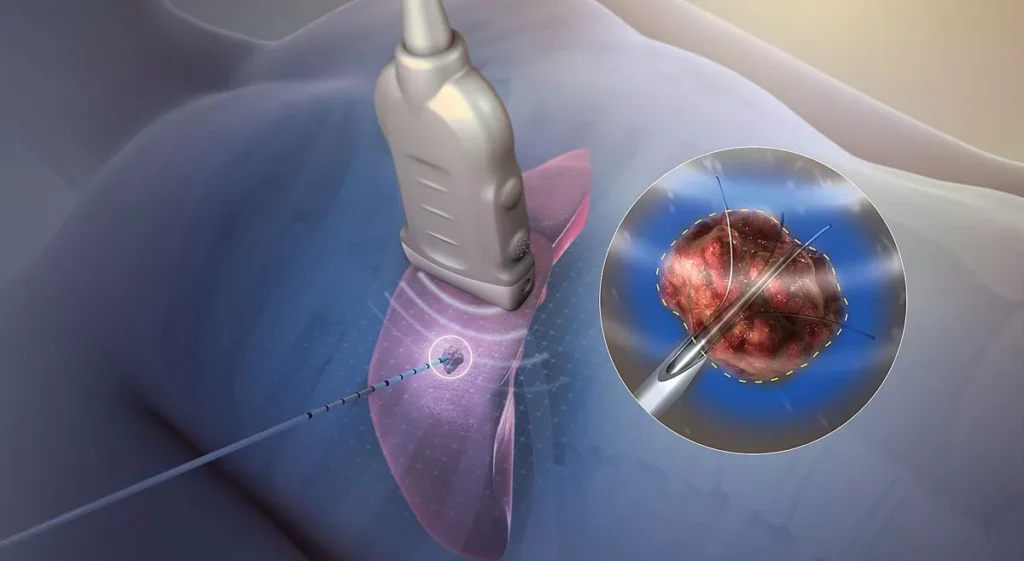
Ablative therapy uses thermal energy (radiofrequency or microwave) to destroy abnormal tissues in the thyroid and liver without open surgery. It’s a game-changing alternative for patients unfit for resection.
Symptoms & Diagnosis:
-
Thyroid nodules: neck swelling, difficulty swallowing
-
Liver tumors: abdominal pain, jaundice
-
Diagnosis via ultrasound, CT, MRI, and biopsy
Procedure Details:
Performed under local anesthesia with real-time image guidance. A probe is inserted through the skin to deliver targeted thermal energy, destroying tumor tissue while preserving surrounding organs.
Benefits:
-
Minimally invasive
-
Quick recovery
-
Daycare procedure
-
Spares healthy tissue
-
Repeatable and safe
Risks & Considerations:
-
Localized pain
-
Mild fever or fatigue
-
Risk of recurrence in aggressive tumors
-
Not suitable for large or deeply situated lesions
Recovery & Aftercare:
Patients go home the same day. Fatigue or mild pain may persist for 1–2 days. Regular imaging follow-up is essential.
Patient Experience:
High success rates in benign thyroid nodules and small liver tumors. Patients appreciate the low risk and short downtime.
FAQs:
Q: What is ablative therapy used for?
A: It treats thyroid nodules and small liver tumors by destroying abnormal tissue using heat.
Q: Will I need general anesthesia?
A: No, the procedure is done under local anesthesia or light sedation.
Q: Is it an alternative to surgery?
A: Yes. Especially beneficial for patients who are not candidates for surgery.